Are you tired of your computer’s sluggish performance? Converting to an M2 SSD could be the answer to your problems. This small but mighty storage device is quickly becoming the go-to for those seeking lightning-fast transfer speeds and improved system responsiveness. Comparable in size to a stick of gum, the M2 SSD offers users higher read and write speeds, faster boot and load times, and lower power consumption than traditional hard drives.
It’s like upgrading from a standard bicycle to a sleek, high-performance racing bike. So, if you’re looking to give your computer a powerful boost and join the ranks of the lightning-fast, read on to learn more about converting to an M2 SSD.
Introduction
If you’re looking to boost your computer’s speed and performance, upgrading to an M.2 SSD drive is a great option. Many people are intimidated by the process of converting to an M.
2 SSD, but it’s actually a fairly straightforward process. First, you’ll need to ensure that your motherboard is compatible with M.2 SSDs.
If it is, you can simply purchase an M.2 SSD and install it into your computer’s M.2 slot.
Once the drive is installed, you’ll need to migrate your operating system and other important files over to the new drive. There are a number of tools available to help you do this, such as Macrium Reflect or Clonezilla. By following these steps, you’ll be able to enjoy faster load times, quicker boot-ups, and improved overall performance on your computer.
So if you’re wondering how to convert to an M.2 SSD, don’t hesitate to give it a try!
Understanding M2 SSDs
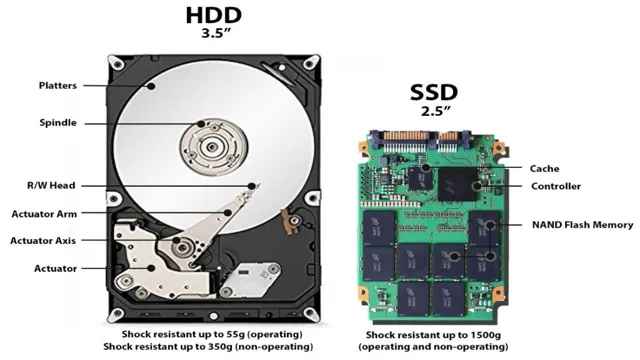
M2 SSDs Introduction: M2 SSDs are one of the most advanced types of solid-state drives available on the market today. They are known for their blazing-fast data transfer speeds, compact size, and low power consumption. M2 SSDs are particularly popular in the gaming and high-performance computing communities, as they allow for lightning-fast boot and load times and quicker access to large files.
But what exactly are M2 SSDs, and how do they work? In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at M2 SSDs and what makes them different from other types of SSDs.

Benefits of Upgrading to M2 SSD
If you’re looking to boost the performance of your computer or laptop, upgrading to an M2 SSD is definitely worth considering. Modern M2 SSDs can deliver high-speed data transfer rates, fast boot times, and improved performance compared to traditional hard drives or even older SSDs. With an M2 SSD, you can expect faster file transfers, faster program loading times, and a more responsive computing experience.
Not to mention, M2 SSDs use less power and generate less heat, which can lead to improved battery life and reduced system noise. By making the switch to an M2 SSD, you can enjoy all these benefits and more, making it an excellent investment for anyone looking to optimize their computer’s performance.
Checking Compatibility
If you’re looking to upgrade your storage options and move to a faster M.2 SSD, one of the first things you’ll need to do is check the compatibility of your system. Before making any purchases, it’s important to make sure that your motherboard supports M.
2 drives and has an available slot for one to be installed. You’ll also want to consider the size of the drive you’re interested in and whether it will fit in your case. Additionally, if you plan to use the drive as your primary boot drive, you’ll need to make sure that your motherboard supports booting from an M.
2 drive. Overall, taking the time to confirm the compatibility of your system can save you a lot of frustration and hassle down the line when trying to install your new drive.
M2 SSD Slot Types
When it comes to adding an M2 SSD to your computer, it’s important to check compatibility before making a purchase. There are different types of M2 SSD slot types, including B key, M key, and B+M key. B key slots only support SATA-based SSDs, while M key slots support both SATA and NVMe-based SSDs.
B+M key slots can accommodate both SATA and NVMe-based SSDs as well, but it’s essential to check the exact specifications of the slot before buying an M2 SSD. Using the wrong type of M2 SSD can lead to compatibility issues and may cause damage to your computer. Therefore, prior research is crucial to ensuring you buy an M2 SSD that is compatible with your computer’s M2 slot.
Checking Motherboard Compatibility
Checking motherboard compatibility is an essential step when building a PC or upgrading an old one. You need to ensure that your motherboard is compatible with all the components you are planning to use, including the processor, RAM, and graphics card. To do this, it’s vital to check the motherboard’s specifications and compare them with those of your other components.
The easiest way to determine motherboard compatibility is to visit the manufacturer’s website and check the specifications listed for your motherboard model. Once you determine which components you’ll be using, ensure they are compatible with your motherboard before purchasing them. It’s better to invest time in checking compatibility beforehand than to end up with a non-working PC due to incompatible components.
Always keep in mind that a PC is like a jigsaw puzzle, and each component must fit together perfectly to create a functional computer.
Installation
If you’re looking to upgrade your computer’s storage by switching to an M.2 SSD, the installation process isn’t as daunting as it may seem. First, you’ll want to ensure your computer’s motherboard supports M.
2 SSDs. Once confirmed, shut down your computer and unplug all cables. Open up the case and locate the M.
2 slot on your motherboard. Carefully insert the M.2 SSD into the slot at a slight angle, ensuring the pins align properly.
Use a retaining screw or clip to secure the M.2 SSD in place. Before closing up the case and reconnecting cables, make sure the M.
2 SSD is recognized in your computer’s BIOS settings. Once confirmed, it’s time to enjoy the faster read and write speeds of your new M.2 SSD.
With the right tools and a little bit of patience, converting to an M.2 SSD should be a breeze.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installation
Installing new components or software on your computer can often feel like a daunting task, especially if you haven’t done it before. However, with just a little bit of guidance and some basic knowledge, it can be a straightforward and painless process. Whether you’re installing a new program or upgrading your hardware, the first step is to ensure that you have all the necessary tools and equipment.
It’s crucial to read the instructions carefully and prepare yourself before starting. For example, if you’re upgrading your CPU, make sure you have a compatible motherboard and enough thermal paste. Similarly, if you’re installing a new program, check the system requirements and make sure that your computer meets them.
Following a step-by-step guide can ensure that you don’t miss any important steps and provide you with the confidence to tackle any installation process on your own.
Cloning Data to M2 SSD
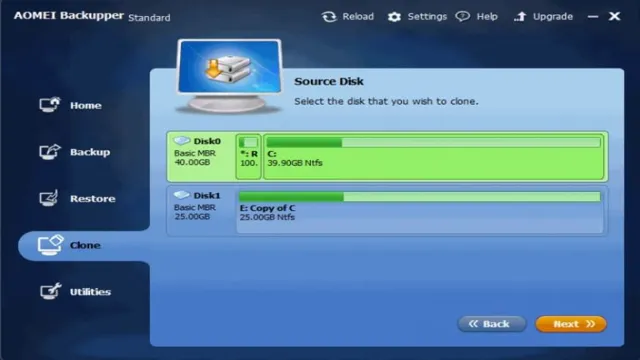
If you’re looking to boost the performance of your computer, one upgrade you can make is replacing your old hard drive with an M2 SSD. Not only do SSDs offer faster read and write speeds, but they also run cooler and are more durable. But what happens to all the data on your old hard drive? That’s where cloning comes in.
Cloning your data means making an exact copy of your current drive and transferring it to the new one. To do this, you’ll need a cloning software and a USB to M2 adapter. Once you have everything you need, simply connect both drives and begin the cloning process.
It’s important to note that the new drive must have sufficient space to accommodate all the data on the original drive. So if you have a 1TB hard drive, you’ll need a 1TB M2 SSD or larger. Once the cloning process is complete, you’ll be able to enjoy faster boot times and improved overall performance without losing any of your precious data.
So what are you waiting for? Upgrade to an M2 SSD today and experience the benefits for yourself!
Conclusion
In conclusion, converting to an M.2 SSD is like upgrading your car’s engine – it’s all about maximizing speed and performance. By following a few simple steps, you can swap out your old hard drive for a sleek and speedy M.
2 SSD that will take your computer to the next level. So if you’re ready to rev up your computer’s performance, it’s time to grab a screwdriver and make the switch to an M.2 SSD.
“
FAQs
What is an m2 SSD?
An m2 SSD is a type of solid state drive that connects directly to the motherboard of a computer via a small form factor M.2 slot.
How can I tell if my computer supports m2 SSDs?
You can usually check your computer’s documentation or specifications to see if it has an available M.2 slot. Alternatively, you can visually inspect the motherboard to see if it has an M.2 slot.
Can I replace my current hard drive with an m2 SSD?
Yes, you can usually replace your traditional hard drive with an m2 SSD, but be sure to check compatibility with your computer’s specifications and ensure that you have the necessary equipment and knowledge for installation.
What are the benefits of using an m2 SSD?
Using an m2 SSD can provide faster performance, improved boot times, and increased storage capacity, all in a smaller and more compact form factor compared to traditional hard drives.