Solid-State Drives (SSDs) have revolutionized the storage landscape, offering significantly faster performance and greater reliability compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). SSDs utilize flash memory, a type of non-volatile memory that stores data electronically.
NAND flash memory is the primary technology used in most modern SSDs. It consists of cells that store data in binary format. Understanding the different types of NAND flash memory, including TLC, QLC, and MLC, is crucial for making informed decisions about SSD purchases.
The choice between TLC, QLC, and MLC SSDs can significantly impact performance, capacity, cost, and overall user experience. By understanding the key differences between these technologies, you can select the SSD that best suits your specific needs and budget.
Understanding NAND Flash Memory
NAND flash memory is a type of non-volatile memory used in SSDs. It’s composed of arrays of memory cells, each capable of storing multiple bits of data. Unlike traditional hard drives with mechanical components, NAND flash memory stores data electronically, making it faster and more reliable.
How NAND Flash Memory Works:
- Cells: NAND flash memory cells are arranged in blocks. Each cell can store a specific number of bits of data.
- Programming: To store data, a voltage is applied to a cell to charge it to a specific level. This level represents a binary value (0 or 1).
- Reading: To read data, a voltage is applied to the cell, and the resulting current is measured to determine the stored value.
- Erasing: Before writing new data to a cell, it must be erased. This process involves clearing all the bits in the cell to a neutral state.
Types of NAND Flash Memory:
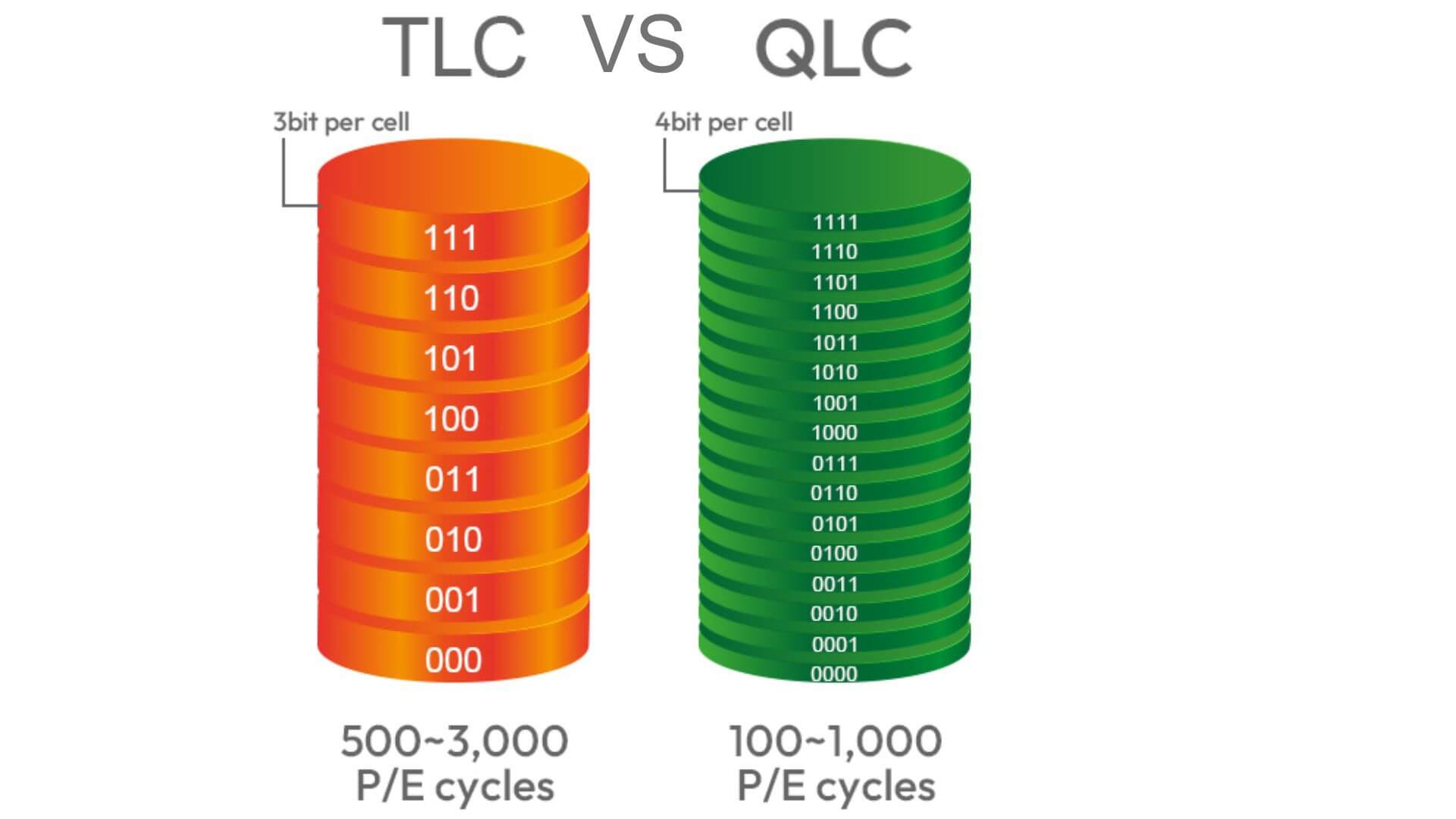
- TLC (Triple-Level Cell): TLC cells can store three bits of data, allowing for higher storage densities but potentially sacrificing performance.
- QLC (Quad-Level Cell): QLC cells can store four bits of data, offering even higher storage densities but with potential performance trade-offs.
- MLC (Multi-Level Cell): MLC cells can store two bits of data, striking a balance between performance and capacity.
TLC SSDs: A Closer Look
TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs are a type of NAND flash memory-based SSD that store three bits of data per cell. This higher storage density allows TLC SSDs to offer larger capacities at a lower cost compared to MLC or QLC SSDs.
Advantages of TLC SSDs:
- Lower cost: Due to their higher storage density, TLC SSDs are generally more affordable than MLC or QLC SSDs, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers.
- Higher capacity: TLC SSDs can offer significantly larger storage capacities compared to their MLC or QLC counterparts, allowing users to store more data on a single drive.
Potential Drawbacks of TLC SSDs:
- Slower performance: TLC SSDs typically have slightly slower read and write speeds compared to MLC or QLC SSDs. This can be noticeable in certain applications, such as gaming or video editing.
- Shorter lifespan: Due to the increased complexity of storing three bits per cell, TLC SSDs may have a slightly shorter lifespan compared to MLC or QLC SSDs. However, modern TLC SSDs have improved endurance and can still provide reliable performance for many years.
While TLC SSDs may have some limitations, they offer a good balance between performance, capacity, and cost for many users. They are particularly well-suited for tasks that prioritize storage capacity over extreme performance.
QLC SSDs: A Closer Look
QLC (Quad-Level Cell) SSDs are a type of NAND flash memory-based SSD that store four bits of data per cell. This even higher storage density allows QLC SSDs to offer even larger capacities at a lower cost compared to TLC or MLC SSDs.
Advantages of QLC SSDs:
- Even lower cost: QLC SSDs are generally the most affordable type of SSD due to their extremely high storage density.
- Even higher capacity: QLC SSDs can offer massive storage capacities, making them ideal for storing large amounts of data.
Potential Drawbacks of QLC SSDs:
- Even slower performance: QLC SSDs typically have the slowest read and write speeds compared to TLC or MLC SSDs. This can be noticeable in performance-intensive applications, such as gaming or video editing.
- Shorter lifespan: Due to the increased complexity of storing four bits per cell, QLC SSDs may have an even shorter lifespan compared to TLC or MLC SSDs. However, recent advancements in QLC technology have improved their endurance and reliability.
While QLC SSDs offer exceptional storage capacity at a low cost, their performance and lifespan may not be suitable for all applications. They are best suited for users who prioritize storage capacity over extreme performance, such as for data storage or less demanding tasks.
MLC SSDs: A Closer Look
MLC (Multi-Level Cell) SSDs are a type of NAND flash memory-based SSD that store two bits of data per cell. This intermediate storage density strikes a balance between performance and capacity, offering a good compromise between TLC and QLC SSDs.
Advantages of MLC SSDs:
- Better performance: Compared to TLC and QLC SSDs, MLC SSDs generally offer faster read and write speeds. This makes them suitable for performance-intensive applications, such as gaming, video editing, and content creation.
- Longer lifespan: MLC SSDs typically have a longer lifespan compared to TLC and QLC SSDs due to the reduced complexity of storing two bits per cell. This means they can withstand more write cycles before experiencing performance degradation.
Potential Drawbacks of MLC SSDs:
- Higher cost: MLC SSDs are generally more expensive than TLC or QLC SSDs, due to their higher performance and longer lifespan.
- Lower capacity: Compared to TLC and QLC SSDs, MLC SSDs offer lower storage capacities for a given physical size. This can be a limitation for users who require massive storage space.
MLC SSDs offer a good balance of performance and capacity, making them a suitable choice for users who prioritize both factors. They are a good option for applications that require moderate to high performance, such as gaming, content creation, or professional use. However, their higher cost may be a consideration for budget-conscious consumers.
Comparing TLC, QLC, and MLC SSDs
| Feature | TLC SSDs | QLC SSDs | MLC SSDs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage density | Highest | Highest | Medium |
| Performance | Lowest | Lower | Highest |
| Cost | Lowest | Lowest | Highest |
| Lifespan | Shortest | Shorter | Longest |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between TLC, QLC, and MLC SSDs:
- Performance: If you require the fastest possible read and write speeds, MLC SSDs are generally the best choice. However, TLC and QLC SSDs have improved significantly in recent years, and the performance gap may be less noticeable for many users.
- Capacity: If you need to store large amounts of data, TLC and QLC SSDs offer the highest capacities. However, MLC SSDs can still provide ample storage for most users.
- Cost: TLC and QLC SSDs are generally more affordable than MLC SSDs, making them a good option for budget-conscious consumers.
- Intended use: Consider your specific needs and the types of applications you’ll be using the SSD for. If you prioritize performance and reliability, MLC SSDs may be the best choice. If you need massive storage capacity at a lower cost, TLC or QLC SSDs could be suitable.
Ultimately, the best SSD for your needs will depend on a combination of factors. Carefully consider your priorities and budget to make an informed decision.
Choosing the Right SSD for Your Needs
Gaming:
- Recommendation: MLC SSDs offer the best balance of performance and reliability for gaming, ensuring smooth gameplay and fast load times. However, TLC SSDs can also be a good option for budget-conscious gamers, especially if you prioritize capacity over extreme performance.
Content Creation:
- Recommendation: MLC SSDs are generally recommended for content creation tasks like video editing, graphic design, and music production, as they provide the necessary performance and reliability. However, TLC SSDs can be a viable option for less demanding content creation workflows.
Data Storage:
- Recommendation: QLC SSDs are excellent choices for data storage due to their massive capacities and affordable prices. They are well-suited for storing large amounts of data, such as media files, documents, or backups.
Everyday Computing:
- Recommendation: TLC SSDs are a great option for everyday computing tasks, offering a good balance of performance, capacity, and cost. They are suitable for tasks like web browsing, office productivity, and light gaming.
Balancing Performance, Capacity, and Cost:
- Performance-oriented users: Prioritize MLC SSDs for the best performance.
- Capacity-focused users: Consider QLC SSDs for their massive storage capacities.
- Budget-conscious users: TLC SSDs offer a good balance of performance and cost.
Remember to consider your specific needs and budget when selecting an SSD. It’s also important to be aware of the latest advancements in SSD technology to ensure you’re making an informed decision.
People Also Ask (PAA) Queries
What is the difference between TLC and QLC SSDs?
- TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs store three bits of data per cell, offering lower cost and higher capacity but potentially slower performance and shorter lifespan.
- QLC (Quad-Level Cell) SSDs store four bits of data per cell, offering even lower cost and higher capacity but with even slower performance and shorter lifespan.
Which type of SSD is best for gaming?
MLC SSDs are generally recommended for gaming due to their better performance and longer lifespan. However, TLC SSDs can also be a good option for budget-conscious gamers, especially if you prioritize capacity over extreme performance.
How long do SSDs last?
The lifespan of an SSD can vary depending on factors like usage, maintenance, and the type of NAND flash memory used (TLC, QLC, or MLC). Generally, SSDs can last for several years, but their lifespan can be shortened by excessive wear and tear or manufacturing defects.
Are TLC SSDs reliable?
TLC SSDs have become increasingly reliable in recent years, with advancements in technology improving their endurance and performance. However, they may still have a slightly shorter lifespan compared to MLC SSDs.
What is the fastest type of SSD?
MLC SSDs are generally considered the fastest type of SSD, offering the best performance for demanding applications like gaming and video editing. However, the performance gap between TLC and QLC SSDs has narrowed in recent years.
Are QLC SSDs worth it?
QLC SSDs can be a good choice for users who prioritize capacity over extreme performance. They offer massive storage capacities at a very affordable price, making them suitable for data storage and less demanding tasks.
What is the difference between MLC and TLC SSDs?
MLC (Multi-Level Cell) SSDs store two bits of data per cell, offering a balance between performance and capacity. TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs store three bits of data per cell, offering higher capacity but potentially lower performance.
Should I buy a TLC or QLC SSD for my laptop?
If you prioritize performance and reliability, an MLC SSD might be a better choice. However, if you need a large storage capacity and are willing to sacrifice some performance, a TLC or QLC SSD could be a suitable option. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs and budget.
Future Trends in SSD Technology
The SSD market is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging to push the boundaries of performance, capacity, and cost. One promising technology that has the potential to revolutionize the SSD industry is 5D NAND.
5D NAND is a type of NAND flash memory that stores data in five dimensions instead of the traditional two or three dimensions used in TLC and QLC SSDs. This increased storage density allows for even higher capacities and potentially lower costs. 5D NAND is still in its early stages of development, but it could significantly impact the SSD market in the coming years.
In addition to 5D NAND, other emerging technologies may also influence the future of SSDs. These include:
- Vertical NAND (VNAND): VNAND technology stacks memory cells vertically, increasing storage density and reducing the footprint of SSDs.
- Phase Change Memory (PCM): PCM is a type of non-volatile memory that offers faster write speeds and potentially longer lifespans compared to NAND flash.
- Memristors: Memristors are a type of memory device that could potentially replace traditional NAND flash memory. They offer high speed, high endurance, and the ability to store analog data.
As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see even higher storage capacities, faster speeds, and lower costs in the SSD market. This will benefit consumers and businesses alike, as SSDs become more accessible and capable of meeting the demands of increasingly data-intensive applications.