If you’re looking to buy a new computer, one of the biggest decisions you’ll need to make is whether you want a Solid-State Drive (SSD) or a Hard Disk Drive (HDD). These two types of storage devices have different strengths and weaknesses, but the biggest difference between them is speed. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the pros and cons of SSD vs HDD, and help you make an informed decision about which one is right for you.
Are you ready to learn more about the speed comparison between SSDs and HDDs? Let’s get started!
What is an SSD?
When it comes to storage technology, you may be wondering how fast an SSD (solid-state drive) is compared to an HDD (hard disk drive). The answer is simple: SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs. This is because SSDs don’t have any moving parts, and data is stored on flash memory chips.
In comparison, HDDs rely on spinning disks to read and write data, which can lead to slower performance. In general, an SSD can be up to 10 times faster than an HDD, which makes it a great choice for anyone who wants their computer to run smoothly and quickly. So, if speed is a priority for you, an SSD is definitely worth considering.
Definition and Benefits
An SSD or a solid-state drive is a storage device that stores data on a solid-state flash memory chip, rather than on a spinning disk like a traditional hard drive. Unlike traditional hard drives, SSDs have no moving parts. This means that they can access data very quickly and are less prone to physical damage caused by bumps and drops.
SSDs are increasingly popular in devices such as laptops and mobile phones due to their speed and reliability. They are also used in high-end gaming computers and servers as they can provide faster data transfer rates, which can improve processing times, reduce lag, and increase overall performance. Overall, SSDs are an excellent choice for those looking for reliable and fast storage solutions.
Data Transfer Rate
Data Transfer Rate SSD Are you tired of your computer taking forever to load programs and files? It’s time to upgrade to an SSD. SSD, or Solid State Drive, is a data storage device that uses flash memory to store and retrieve data. Unlike traditional hard drives, which have mechanical parts that can slow down data transfer, SSDs rely on memory chips that can access data almost instantly.
This means faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and smoother multitasking. Plus, SSDs are more durable and reliable than hard drives, since they don’t have moving parts that can break down. So if you want to take your computer to the next level, consider investing in an SSD.
With its lightning-fast data transfer rate, you’ll never have to wait for your computer to catch up with you again.
What is an HDD?
When it comes to storage devices, two main types come to mind – the solid-state drive (SSD) and the hard disk drive (HDD). The key difference between the two is the way they use data storage. SSDs use flash memory chips while HDDs store data on a spinning metal disk.
As you might expect, this difference has a significant impact on their performance levels. When it comes to speed, SSDs win hands down over HDDs, making them the preferred choice for many computer users. You’ll be able to boot up your computer in seconds instead of minutes, and programs will launch instantly.
In comparison, an HDD can take a few extra seconds to get going. When it comes to how fast is SSD compared to HDD, the difference is night and day. Therefore, if you’re looking for fast data access and retrieval, an SSD is the way to go.
Definition and Drawbacks
An HDD, or Hard Disk Drive, is a type of data storage device commonly used in computers and other electronic devices. It consists of one or more spinning disks coated with magnetic material that stores data in patterns of tiny magnetized areas. The data is read and written to the disk using a magnetic head positioned very close to the surface of the disk.
While HDDs are a popular choice due to their low cost and high storage capacity, they also have some drawbacks. Since the read/write head needs to physically move across the disk, HDDs can be slow in accessing data. They are also prone to mechanical failure, as the spinning disks and moving parts can be easily damaged.
Additionally, they are not very portable due to their size and weight, making them less practical for use in laptops and other portable devices. Despite these limitations, HDDs continue to be widely used and are a reliable and affordable option for storing large quantities of data.
Data Transfer Rate
Data Transfer Rate An HDD or Hard Disk Drive is a data storage device that uses magnetic storage to store and retrieve digital information. It is made up of one or more rotating disks that are coated with a magnetizable substance. These disks spin at high speeds, and data is read and written to the disks using a magnetic head that moves back and forth across the surface of the disks.
The speed at which data is transferred to and from the hard disk is known as the data transfer rate. This rate is measured in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s) and is determined by the speed of the disk’s rotation and the size of the cache. The higher the data transfer rate, the faster the computer can access the data on the hard disk.
For those who want to work with large files and data-intensive applications, a higher data transfer rate may be required to ensure the best performance. In summary, an HDD is a fundamental component of any computer system, and its data transfer rate impacts the speed and efficiency of the computer.
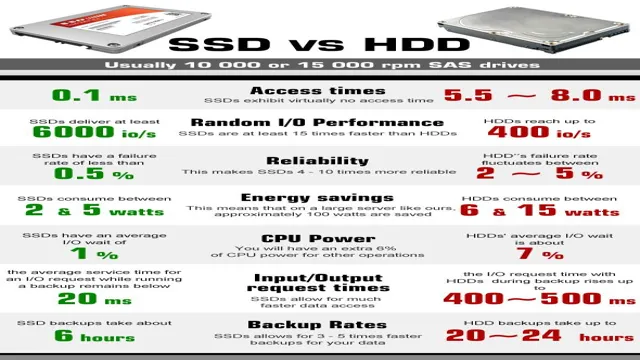
SSD vs HDD Speed Comparison
Are you wondering how fast is SSD compared to HDD? Well, the answer is that SSDs are significantly faster and more efficient than traditional HDDs. SSDs use flash memory to store data, while HDDs use spinning disks or platters. This means that when you access data on an SSD, there is no mechanical movement required, which leads to faster read and write speeds.
Additionally, SSDs have no fragmentation issues, as the data is stored in a continuous block. This also leads to faster access times, as the system can read the data faster without having to search for it. Overall, SSDs are the superior option when it comes to speed and performance, making them a popular choice for gamers and professionals who require fast access to large amounts of data.
So, without any doubt, SSDs are faster than HDDs when it comes to accessing data.
Boot Time
One of the significant advantages of SSDs over HDDs is their speed. SSDs are known to have a quicker boot-up time compared to HDDs. Unlike HDDs, which rely on spinning disks for data retrieval and storage, SSDs use flash memory, which makes them faster and more efficient.
While an HDD can take up to several minutes to boot up, an SSD can boot up in seconds. This means that when you turn on your computer or laptop, you don’t have to wait around for long before you can start working or browsing the internet. If you’re someone who values speed and efficiency, choosing an SSD over an HDD is a wise choice.
Loading Programs and Files
When it comes to loading programs and files, the type of storage device you use can have a big impact on speed and performance. SSDs (solid-state drives) are becoming increasingly popular due to their impressive speed and efficiency. In fact, SSDs are often considered up to 10 times faster than traditional HDDs (hard disk drives) in terms of read and write speeds.
This means that loading programs and files on an SSD can be lightning fast, improving overall system performance and productivity. However, it’s worth noting that SSDs are typically more expensive than HDDs and don’t have as much storage capacity. Deciding which type of storage device to use ultimately depends on your specific needs and budget.
So, whether you’re a gamer, a content creator, or just a casual computer user, choosing the right storage device for your needs can make all the difference in terms of speed and efficiency.
Data Transfer Rate Comparison
When it comes to comparing the data transfer rates of SSDs and HDDs, there is a clear winner. Solid-state drives, or SSDs, are known for their blazing-fast speed and high performance. They utilize flash memory to store data, which means there are no moving parts.
On the other hand, hard disk drives, or HDDs, consist of spinning disks and mechanical read/write heads. This can result in slower read and write speeds. Overall, SSDs are capable of much faster data transfer rates than HDDs.
In fact, SSDs can transfer data at rates up to 6 gigabytes per second, while HDDs typically top out at around 200 megabytes per second. So if you’re looking for speed and performance, an SSD is definitely the way to go.
Conclusion
In the race between SSD and HDD, the finish line is clear: SSD takes the crown for speed and performance. The difference is like a tortoise and hare scenario, with SSD being the hare that zips ahead at breakneck speeds while HDD plods along like a tortoise. So if you want lightning-fast data access and snappy system performance, SSD is the way to go.
But if you don’t mind waiting a bit longer and saving a few coins, HDD might be the tortoise for you. Just beware, in today’s fast-paced world, being a tortoise might not cut it for long.”
FAQs
What is the speed difference between SSD and HDD?
SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs, with read and write speeds typically between 200-550 MB/s and 100-500 MB/s respectively. Meanwhile, HDDs have read and write speeds ranging from 50-120 MB/s.
How does SSD speed affect overall system performance?
SSD speed can greatly improve overall system performance, as it reduces the time it takes to load applications, boot up the system, and transfer files. This can lead to a faster, more responsive computing experience.
Are there any downsides to using an SSD instead of an HDD?
The main downside to using an SSD is the cost, as they are typically more expensive than HDDs per GB of storage. Additionally, SSDs have a limited number of write cycles before they begin to degrade, although this is less of an issue with newer SSDs.
Can you use both an SSD and an HDD together in a computer?
Yes, it is possible to use both an SSD and an HDD together in a computer. This is often done by installing the operating system and frequently used applications on the SSD for faster access, while using the HDD for storing larger files and long-term storage.
