Are you looking for ways to format your M2 SSD? Well, you’ve come to the right place. Like any other storage device, an M2 SSD needs to be formatted for it to work correctly. It can be a bit nerve-wracking for first-timers, but we’ve got you covered.
Think of it as cleaning out your closet, but instead of organizing clothes, you’re organizing data. It’s like starting fresh with a new pair of sneakers; it’ll feel like you have a brand new device. Formatting your M2 SSD can solve performance issues, and it’ll free up some space that you might not even know you had! Sounds fantastic, right? Before diving into formatting your M2 SSD, it’s essential to know the ins and outs of the process.
We’re here to guide you through how to format your M2 SSD effortlessly. In this article, we’ll provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to format your M2 SSD and explain why it’s necessary. We’ll also give you a heads up on the potential pitfalls and what to do if things don’t go as planned.
By the end of this article, you will be able to format your M2 SSD without breaking a sweat! So, let’s get started!
Understanding M2 SSDs
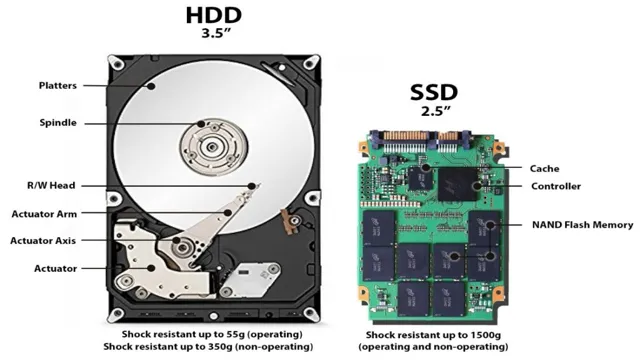
If you’re looking to format your M2 SSD, it’s important to understand what it is and how it works. M2 SSDs refer to a type of solid-state drive that is typically smaller and faster than other forms of SSDs. Because of their smaller size, they’re often used in laptops and other devices where space is limited.
However, formatting an M2 SSD is very similar to formatting any other type of hard drive. You’ll need to initialize the drive, create a partition, and then format the partition with a file system. It’s important to note that formatting an M2 SSD will erase all data on the drive, so make sure you back up any important files beforehand.
Once it’s formatted, you can use your M2 SSD for storing data, running programs and applications, or even as a boot drive for your operating system. Overall, if you need to format your M2 SSD, it’s a straightforward process that can be completed quickly and easily.
Benefits of M2 SSDs
M2 SSDs M2 SSDs are revolutionizing the way we store our data. These small, but powerful solid-state drives are becoming increasingly popular due to their impressive speed, reliability, and efficiency. They utilize the M2 interface, which connects directly to the motherboard, allowing for faster data transfer rates compared to traditional hard drives.
M2 SSDs also offer higher capacity and better endurance, making them ideal for users who require high-performance storage for demanding tasks. They can be used in laptops, desktops, and even some high-end gaming consoles. Moreover, M2 SSDs are designed to be low profile, making them an excellent option for small form factor builds.
In summary, M2 SSDs are a game-changer in the world of data storage, providing users with fast, reliable, and efficient storage solutions.
Types of M2 SSDs
M2 SSDs M2 SSDs come in different types that cater to different needs, and understanding the differences can help you choose the right one. M2 SSDs can be categorized based on their interface and key, with the most common being PCIe and SATA. PCIe SSDs are faster and more expensive than SATA SSDs and require a PCIe slot on your motherboard.
SATA SSDs, on the other hand, are slower and less expensive and can be used with a SATA slot. M2 SSDs also vary in key design, with M key and B key being the most popular. M-key SSDs support PCIe and NVMe, while B-key SSDs support SATA.
M2 SSDs can also come in different lengths, with 2260 and 2280 being the most common. In summary, when choosing an M2 SSD, consider the interface, key, and length based on your intended use and motherboard compatibility.
Formatting M2 SSD
If you’re struggling with slow load times and lag on your M2 SSD, formatting the drive might be the solution to your problems. The process is relatively straightforward and can be done with just a few clicks. First, navigate to your computer’s disk management utility.
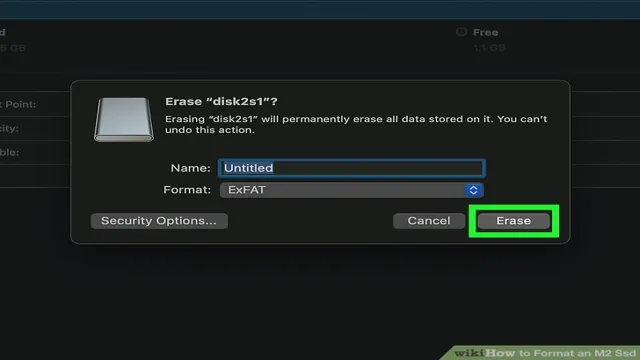
From there, find your M2 SSD and right-click to bring up the formatting options. Make sure to choose the correct file system (NTFS or exFAT) and allocation unit size for your needs. Keep in mind that formatting will erase all data from the drive, so make sure to back up any important files beforehand.
Once you’ve selected your options, click format and wait for the process to complete. After formatting, you’ll have a fresh, clean drive that should perform much better than before. With just a little bit of effort, you can breathe new life into your M2 SSD and enjoy faster speeds and smoother performance.
Backup Data
Backing up your data is crucial to protect it from being lost or corrupted, especially when formatting your M2 SSD. Before formatting your M2 SSD, make sure to back up your data to an external drive or cloud storage so that you can easily restore it later. Formatting your M2 SSD will erase all the data on it, so it’s essential to have a backup.
It’s also a good idea to check that your backup is complete and accurate, so you don’t miss any important files. Once you’ve backed up your data, you can proceed with formatting your M2 SSD. This process will efficiently erase all the data on it and restore it to its original state.
So, don’t forget to backup your data before formatting your M2 SSD to ensure that you don’t lose any important files.
Partition M2 SSD
Partitioning an M2 SSD may seem like a daunting task, but it is actually quite simple. The first step is to format the SSD, which involves erasing all data on the drive and preparing it for use. This can be done through the built-in formatting tool on your operating system or through a third-party software.
Once the drive is formatted, you can then partition it into separate sections, each with their own drive letter and allocation of storage space. This is useful for organizing files and programs or creating separate boot partitions for multiple operating systems. It is important to note that partitioning a drive can also affect its performance, so it is recommended to do research beforehand and consult with a professional if necessary.
However, with the right tools and knowledge, partitioning your M2 SSD can be a simple and effective way to optimize your computer’s storage capabilities.
Format M2 SSD using Disk Management
Formatting an M2 SSD can be done easily using Disk Management on Windows. First, ensure that the M2 SSD is properly installed on the motherboard. Then, open Disk Management by right-clicking on the Windows Start menu and selecting the “Disk Management” option.
Find the M2 SSD in the list of available disks and right-click on it. Select the “Format” option, choose the file system you want to use (such as NTFS), and assign a drive letter. You can also give the drive a label if you want.
After confirming the settings, click “OK” to start formatting the M2 SSD. It may take several minutes to complete, depending on the size of the drive. Once the process is finished, the M2 SSD will be ready for use as a new storage device.
Remember to back up any important data before starting the formatting process. By following these steps, you can easily format your M2 SSD and enjoy optimal performance.
Final Thoughts
If you’ve recently purchased a new M.2 SSD and need to format it, then you’re in luck because it’s a relatively simple process. The first step in this process is to backup any important data you have on your drive.
This is especially important if you’re planning to do a clean install of your operating system as this will erase all data on the drive. Once you’ve backed up your data, you’ll need to access Disk Management in Windows. From there, you’ll need to locate your M.
2 SSD and right-click on it to select the “Format” option. This will prompt you with several options such as file system, allocation unit size, and volume label. It’s recommended to choose NTFS as your file system and leave the other options as default unless you have specific needs.
Once you’ve made these selections, click “OK” and the formatting process will begin. Within a few minutes, your M.2 SSD will be fully formatted, and ready to use.
With these simple steps, you can quickly and easily format your M.2 SSD and enjoy faster read and write speeds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, formatting an M.2 SSD is as easy as a few clicks and takes mere seconds. With the right tools and a bit of know-how, you can optimize your SSD for peak performance and enjoy lightning-fast speeds.
So go forth and format your M.2 SSD with confidence – your data (and your computer) will thank you for it!”
FAQs
1. What are the advantages of using an M.2 SSD? A: The M.2 SSD is faster than a traditional hard drive and can also offer improved system boot and application load times. 2. Can I use an M.2 SSD with any motherboard? A: Not all motherboards support M.2 SSDs, so it’s important to check your motherboard specifications before purchasing one. 3. What is NVMe and how does it differ from SATA? A: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a newer interface that allows faster data transfer speeds than the older SATA interface. 4. How do I install an M.2 SSD in my computer? A: Installation instructions can vary depending on your system, but typically involve inserting the M.2 SSD into the appropriate slot and securing it in place with a screw. It’s important to consult your motherboard manual for specific instructions. 5. What should I look for when choosing an M.2 SSD? A: Factors to consider include capacity, read/write speeds, and whether the SSD is compatible with your motherboard interface. It can also be helpful to read reviews and compare prices across different brands and models. 6. Can I use an M.2 SSD as a boot drive? A: Yes, an M.2 SSD can be used as a boot drive, which can help improve system startup times and overall performance. However, be sure to consult your motherboard manual or manufacturer’s website for instructions on how to set up an M.2 SSD as a boot drive.