Are you planning to upgrade your computer’s hard drive to a Samsung SSD and wondering how to migrate your operating system? Migrating your operating system to an SSD can improve your computer’s performance and reduce boot time significantly. However, the process can be overwhelming, especially if you are not tech-savvy. In this article, we’ll guide you through the step-by-step process of migrating your operating system to a Samsung SSD.
Understanding the Migration Process
Before we dive into the migration process, it’s essential to understand what it entails. Migrating your operating system to a Samsung SSD involves transferring all your operating system files, applications, and user data from the current hard drive to the Samsung SSD. There are two primary methods to migrate your operating system to a Samsung SSD: cloning and fresh installation.
Cloning Your Hard Drive
Cloning is the process of creating an exact copy of your hard drive on the Samsung SSD. This method is ideal if you want to migrate your operating system along with your files, applications, and settings. To clone your hard drive, you’ll need a Samsung SSD, cloning software, and a SATA-to-USB cable.
Fresh Installation
A fresh installation involves installing a new copy of the operating system on the Samsung SSD and reinstalling all your applications and settings. This method is ideal if you want a clean slate and don’t want to migrate unnecessary files and settings.
Migrating Your OS to a Samsung SSD – Step by Step Guide
Now that we’ve covered the basics let’s dive into the step-by-step process of migrating your operating system to a Samsung SSD. We’ll cover both cloning and fresh installation methods.
Cloning Your Hard Drive
- Back up your files – Before you start the cloning process, back up all your files, applications, and settings.
- Connect the Samsung SSD – Connect the Samsung SSD to your computer using a SATA-to-USB cable.
- Download cloning software – Download Samsung Data Migration software from the Samsung website.
- Install and launch Samsung Data Migration – Install the software and launch it.
- Select source and destination drive – Select your current hard drive as the source drive and Samsung SSD as the destination drive.
- Start the cloning process – Start the cloning process and wait for it to complete.
- Restart your computer – Once the cloning process is complete, restart your computer and change the boot order to boot from the Samsung SSD.
Fresh Installation
- Back up your files – Before you start the fresh installation process, back up all your files, applications, and settings.
- Create a bootable USB drive – Create a bootable USB drive with Windows installation media.
- Connect the Samsung SSD – Connect the Samsung SSD to your computer using a SATA-to-USB cable.
- Boot from the USB drive – Boot your computer from the USB drive and select the Samsung SSD as the installation drive.
- Install Windows – Follow the on-screen instructions to install Windows on the Samsung SSD.
- Reinstall applications and settings – Once Windows is installed, reinstall all your applications and settings.
Update Drivers and Settings
Once Windows is installed, you should update your drivers and settings. This will ensure that your computer is running optimally on your Samsung SSD. To do this, follow the steps below:
- Go to the Device Manager and update your drivers.
- Go to the Power Options and select “High Performance” mode.
- Disable unnecessary startup programs.
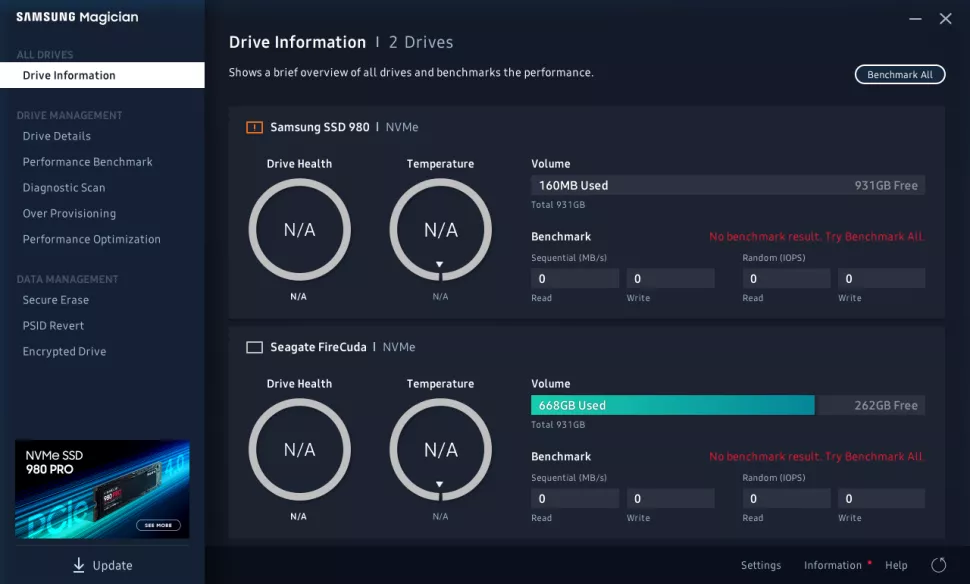
Optimize Your Samsung SSD
To optimize your Samsung SSD, you can use the Samsung Magician software. This software provides several features to improve the performance of your SSD. Follow the steps below to optimize your SSD:
- Download and install Samsung Magician software.
- Launch the software and click “Optimize”.
- Enable features such as “Rapid Mode” and “Over Provisioning”.
Tips and Tricks
Migrating your operating system to a Samsung SSD can be a daunting process, but here are some tips and tricks to make it easier:
- Before you start the migration process, check the compatibility of your computer with the Samsung SSD.
- Ensure that you have a backup of all your important files and data before you start the migration process.
- Use a SATA-to-USB cable to connect the Samsung SSD to your computer.
- Use Samsung Data Migration software for cloning your hard drive.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, migrating your operating system to a Samsung SSD can greatly improve the performance of your computer. It may seem like a daunting process at first, but by following the tips and tricks outlined in this article, you can make the migration process much easier. Before starting the process, it is important to check the compatibility of your computer with the Samsung SSD and to backup all your important files and data. You can use a SATA-to-USB cable to connect the Samsung SSD to your computer and use Samsung Data Migration software for cloning your hard drive. With these steps, you can enjoy the benefits of faster boot and load times, increased productivity, and more storage space. So, don’t hesitate to make the switch to a Samsung SSD today!
FAQs:
- Do I need to reinstall Windows after migrating to a Samsung SSD?
- No, you do not need to reinstall Windows after migrating to a Samsung SSD. You can use Samsung Data Migration software for cloning your hard drive and keep all your files and settings intact.
- Can I migrate my operating system to a Samsung SSD on a laptop?
- Yes, you can migrate your operating system to a Samsung SSD on a laptop as long as it is compatible with the SSD and you have the necessary tools.
- Will migrating to a Samsung SSD improve the performance of my computer?
- Yes, migrating to a Samsung SSD can greatly improve the performance of your computer by increasing boot and load times and providing more storage space.
- Can I use Samsung Data Migration software on a Mac?
- No, Samsung Data Migration software is only compatible with Windows operating systems.
- Is it necessary to use a SATA-to-USB cable for the migration process?
- Using a SATA-to-USB cable can make the migration process much easier, but it is not absolutely necessary. You can also use an external enclosure or an adapter to connect the Samsung SSD to your computer.