Have you ever heard of network storage? It’s a term that’s quickly gaining popularity in the world of technology, and for good reason. With the ever-increasing dependency on digital systems and data, it has become critical for companies and individuals alike to find ways to efficiently store and manage their data. Network storage offers a solution to this problem by providing a centralized storage system that allows multiple users to access and share data simultaneously.
However, not all network storage is created equal, and there are various types to consider. In this blog post, we’ll explore the different types of network storage available and help you determine which one might be the best fit for your needs. So, without further ado, let’s dive in!
Direct Attached Storage (DAS)
When it comes to types of network storage, Direct Attached Storage (DAS) is a great option to consider. With DAS, the storage device is directly connected to a computer or server, providing fast and reliable access to data without the need for a network connection. There are various types of DAS, including external hard drives and solid-state drives, which are great for portable storage and backups.
In addition, there are also rack-mounted servers and storage arrays that offer even higher capacities and more advanced features for businesses with larger storage needs. While DAS may not provide the same level of accessibility and scalability as other types of network storage, it is a great option for those who need fast and reliable access to their data without the need for a network.
Overview
Direct Attached Storage (DAS) is a computer storage technology that connects a computer system directly to physical storage devices. It is a type of external hard drive that is directly attached by a cable or through a port, rather than being accessed over a network. DAS is an excellent option for those who need to store and manage data, such as photos, videos, or music, without the complexity of networking.
DAS devices come in various forms, including USB and Thunderbolt external hard drives, solid-state drives (SSD), and RAID systems. They provide faster data transfer rates than network-attached storage (NAS) systems and can be easily and quickly connected to your computer, making them ideal for tasks that require a lot of data processing, such as video editing, game development, and graphic design. Whether you are a professional requiring high-performance storage or just someone who needs a simple and reliable system for backing up data, DAS is an ideal solution.

Benefits and Drawbacks
Direct Attached Storage (DAS) Direct Attached Storage or DAS is a storage solution that directly connects to a single computer or server via a cable. One of the main benefits of DAS is its fast data transfer speed due to the direct connection, making it ideal for applications that require high-performance data access. DAS is also easy to set up, configure and use, as it does not require additional hardware or software.
However, one of its disadvantages is its limited scalability, as it can only be connected to a single device, making it a poor choice for larger organizations with multiple users and devices that require access to data. Additionally, DAS lacks the redundancy that networked storage solutions offer, making it more susceptible to data loss in the event of a hardware failure or disaster. Despite its drawbacks, DAS is still a useful storage solution for individuals or small businesses with modest storage needs and a limited budget.
Examples – External Drives, USB
When it comes to storage solutions for your computer, Direct Attached Storage (DAS) is an excellent option. DAS includes external hard drives and USB drives, which connect directly to your computer for quick and easy access to your files. These drives provide an additional layer of backup and storage, which is especially helpful for professionals or those who work with large files.
External hard drives generally have larger storage capacities compared to USB drives, but USB drives are smaller and more portable. Both are easy to use and offer convenient ways to store and transfer data. So whether you need to back up important files, transfer data between devices, or simply expand your storage capacity, DAS provides a reliable and accessible solution.
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
When it comes to network storage, there are several options available, one of which is Network Attached Storage (NAS). NAS is essentially a centralized storage system that connects to a network, allowing multiple users to access the stored data. There are two main types of NAS: consumer-grade and enterprise-grade.
Consumer-grade NAS is designed for home or small office use and typically comes with basic features and limited storage capacity. Enterprise-grade NAS, on the other hand, is more robust and designed for larger organizations with higher storage needs. It is scalable, highly available, and offers advanced features such as data encryption and automated backups.
Ultimately, the type of NAS you choose will depend on your specific needs and budget. A good starting point is to consider factors such as the number of users, the amount of data you need to store, and the level of security you require. By doing so, you can choose the right network storage solution to meet your needs while ensuring optimal performance and scalability as your organization grows.
Overview
Network Attached Storage (NAS) is an incredibly versatile solution for those who need reliable data storage. NAS is essentially a standalone device that connects to a network to enable multiple users and computing devices to access the data contained within. It’s a great way to centralize and share files, whether it’s for personal use or in a business setting.
Unlike other storage solutions, NAS is designed to be always on and available, allowing users to access the data they need at any time. With its powerful hardware and software features, NAS can also be used as a media server and for backing up important files. So, if you’re looking for a secure and reliable way to store and share your data, NAS is definitely worth considering.
Benefits and Drawbacks
When it comes to managing and storing data, Network Attached Storage (NAS) offers numerous benefits. Perhaps the most significant advantage of NAS is its ability to centralize data storage and make it accessible to multiple devices. This makes it easier to share files and collaborate on projects, particularly in a work setting.
Additionally, NAS can automate backups and data transfers, which can save time and reduce the risk of data loss. However, there are also some drawbacks to consider. One potential issue is that NAS devices can be expensive, especially if you need a lot of storage.
Additionally, they require some technical knowledge to set up and maintain, which may be daunting for some users. Overall though, the benefits of NAS make it a valuable investment for many businesses and individuals looking for reliable and accessible data storage.
Examples – WD MyCloud, Synology DiskStation
When it comes to storing and managing data, Network Attached Storage (NAS) is an essential tool. It allows multiple devices to access files and data from a centralized location, which can be incredibly convenient for those who work with large amounts of data. Two popular examples of NAS systems are the WD MyCloud and the Synology DiskStation.
Both systems provide users with easy access to their files and data, as well as a variety of features such as file sharing, backup solutions, and mobile access. The WD MyCloud is a great option for those who need a simple and affordable storage solution, while the Synology DiskStation is more feature-rich and ideal for small businesses. Overall, NAS is a reliable and efficient way to manage your data and ensure that it is easily accessible from any device.
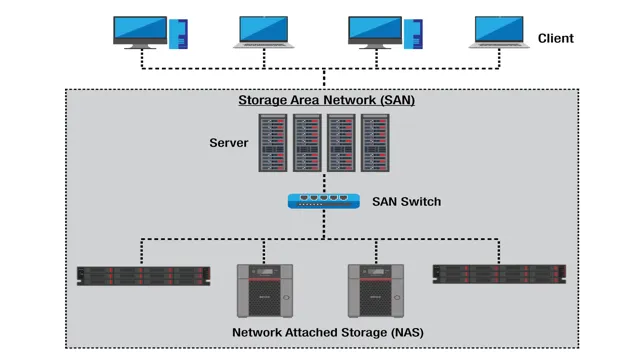
Storage Area Network (SAN)
When it comes to choosing the right type of network storage for your business needs, it’s important to consider all of your options. One popular choice is a Storage Area Network (SAN), which is used to connect servers to a shared pool of storage devices. SANs can be configured using various protocols such as Fibre Channel (FC), iSCSI, or FCoE, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
FC SANs are known for their high-speed performance and low latency, making them ideal for high-performance applications like database hosting. On the other hand, iSCSI SANs offer more flexibility in terms of scalability and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for small to medium-sized businesses. FCoE SANs combine the benefits of both FC and iSCSI, making them a great choice for businesses that want the performance of FC with the cost savings of iSCSI.
When deciding which type of SAN to use, it’s important to consider your business needs and budget to ensure you choose the right solution.
Overview
If your business deals with a large amount of data and requires quick access to it, then a Storage Area Network (SAN) may be the perfect solution for you. A SAN is a dedicated network that provides access to block-level storage devices like disk arrays and tape libraries. It allows multiple servers to access the same storage pool, resulting in a more efficient utilization of storage resources and easier management.
SANs are often used by data centers and businesses that handle large scale data processing. It provides a reliable and scalable method of data management that can easily adapt to the changing needs of the business. So, if you’re looking for a storage solution that provides high performance and scalability, then a SAN may be the right choice for you.
Benefits and Drawbacks
When it comes to data centers and business networks, one technology that has become increasingly popular is the Storage Area Network (SAN). A SAN is a centralized system that stores and manages data, making it easily accessible to all servers and applications on a network. One of the primary benefits of a SAN is its ability to provide high speed, scalable and efficient storage that can scale to accommodate large enterprise environments with ease.
Additionally, SANs offer enhanced protection and data security, making them an ideal choice for businesses that rely on mission-critical applications and data. However, SANs also come with a few drawbacks, including their high cost and complex setup and maintenance. Moreover, SANs require a specialized IT/cybersecurity team to manage because of their complexity.
Nonetheless, with effective management and careful planning, a SAN can be a very beneficial addition to any organization’s technological infrastructure.
Examples – Cisco MDS, Dell EMC Unity
The Cisco MDS and Dell EMC Unity are two examples of Storage Area Network (SAN) products that businesses rely on for efficient and secure data storage. SANs provide block-level access to data storage and are commonly used in large data center environments. The Cisco MDS is a series of multilayer switches that offer high-density storage connectivity and robust security features.
Its management software, Cisco Data Center Network Manager (DCNM), allows for centralized management of multiple SAN switches and simplifies configuration tasks. The Dell EMC Unity, on the other hand, is a midrange SAN solution that provides unified storage for block and file workloads. Its simplified management interface and flexible scalability make it an attractive option for small to midsize businesses.
Both the Cisco MDS and Dell EMC Unity demonstrate the importance of SANs in modern data storage and management.
Conclusion
Overall, we can see that there are many different types of network storage available, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. From cloud storage to NAS devices, there is no shortage of options for storing and organizing our digital lives. And just like any good network, the key is to find the right combination of tools and technologies to ensure the smooth and efficient flow of data.
So whether you’re a data hoarder or a minimalist, there’s a network storage solution out there for everyone. Just remember, with great storage power comes great responsibility to back up your files!”
FAQs
What is Direct Attached Storage (DAS)?
Direct Attached Storage (DAS) is a storage device that is directly attached to a single computer or server. It typically uses USB, SCSI, or SATA connections.
What is Network Attached Storage (NAS)?
Network Attached Storage (NAS) is a storage device that is connected to a network, providing access to multiple users and devices. It typically uses Ethernet connectivity.
What is Storage Area Network (SAN)?
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a high-speed network that connects multiple storage devices to multiple servers, allowing for centralized storage management.
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud Storage is a service that allows users to store and access data online, using a network of remote servers. It allows for scalable and flexible storage options without the need for on-site hardware.
What is Object Storage?
Object Storage is a storage architecture that stores data as objects rather than files, allowing for more efficient and scalable storage. It is often used for large-scale data storage and retrieval.